ECG-NOMENCLATURE
In this article we are going to study how to identify a particular wave among the important five waves namely P, Q, R, S, T.
At any time when we examine the ECG we should always note that the first wave of the heartbeat as shown in the figure should be identified as P-waves. The P-waves appear in many forms as shown below.
 |
| FIG-1 |
The above figure (Fig-1) note that the P-waves are in different forms. Except for the first one all three are abnormal P-waves. At the last abnormal P-wave, the P-wave is almost absent.
As we already studied from the last posts about ECG that the P-wave represents the contraction (depolarization)of the upper chambers (Atria) of the heart. Hence any irregular abnormal P-waves are seen in the ECG then it means there are problems in any one of the atria or both. If there is a conical shaped apex in the P-wave (Fig-1-1st abnormal) it means the right atrium is enlarged.
If there is an M-shaped apex in the P-wave (2nd abnormal in Fig-1) it means the left atrium is enlarged.
If the P-wave is overlaid on the baseline, disappeared, or almost absent(3rd abnormality-Fig-1) then SA nodal blockade and atrial fibrillation must be suspected. In atrial fibrillation the P-wave is replaced by tiny irregular f-waves.
The next wave follows is the Q-wave which forms a part of the important QRS-complex.
The Q-wave can be defined in two ways.
1.Q-wave is the wave with a minute or large negative deflexion following the P-wave. or
2. The Q-wave can be defined as the wave with a small or large negative deflection which is immediately followed by the R-wave.In other words
Any negative deflection whether it is small or large immediately before R-wave should be identified as Q-wave or 'q'-wave if it is small
QRS-Nomenclature
As we know that the QRS-complex is the main part of the ECG so we should deal with a special for it as follows:-
Three things we must keep in our minds.
1.Position of the waves
2.Nature of deflection (+ or -)
3.Size of the deflection.
See the following figures Fig-2; and Fig-3.Fig-4; and Fig-5.
See the above Fig-2 a normal QRS complex is displayed.
In the above figure (Fig-3)there is a typical QRS complex is displayed. Sometimes we come across such complicated ECGs to identify the waves.
In such cases we should always devise a common theory which states that in any QRS- complex the first negative deflection immediately before the R-waves must be named as Q or q-waves depending upon the size of the deflection. If there are more than one it should be quoted with ' (prime)
Note in the above figure (Fig-3) the Q-wave is absent as there is no first negative deflection before R-wave.
Secondly in any QRS complex any first positive deflection within the complex should be named as R or r waves with ' (prime) if there are more than one according to its sizes.
See the following another typical QRS.
Thirdly any first negative deflection immediately after the R-wave is the S or s waves with '(prime)
if more than as per its sizes.
In the above figure (FIG-4) again there are no Q-waves. But there are 2 consecutive positive deflections represents two R-waves (R, R') immediately followed by two consecutive negative deflections named as S and S'.
Then the nomenclature of the T-wave which represents the relaxation of the ventricles.
In the above figure note the position deflection of the T-wave. After the T wave, after the ventricular relaxation there is no electrical conduction up to the next cycle started by the SA-node the pacemaker. Hence the interval T-P is the perfect and absolute iso electrical line to be kept for reference.
Continued in next post(F)
As we already studied from the last posts about ECG that the P-wave represents the contraction (depolarization)of the upper chambers (Atria) of the heart. Hence any irregular abnormal P-waves are seen in the ECG then it means there are problems in any one of the atria or both. If there is a conical shaped apex in the P-wave (Fig-1-1st abnormal) it means the right atrium is enlarged.
If there is an M-shaped apex in the P-wave (2nd abnormal in Fig-1) it means the left atrium is enlarged.
If the P-wave is overlaid on the baseline, disappeared, or almost absent(3rd abnormality-Fig-1) then SA nodal blockade and atrial fibrillation must be suspected. In atrial fibrillation the P-wave is replaced by tiny irregular f-waves.
The next wave follows is the Q-wave which forms a part of the important QRS-complex.
The Q-wave can be defined in two ways.
1.Q-wave is the wave with a minute or large negative deflexion following the P-wave. or
2. The Q-wave can be defined as the wave with a small or large negative deflection which is immediately followed by the R-wave.In other words
Any negative deflection whether it is small or large immediately before R-wave should be identified as Q-wave or 'q'-wave if it is small
QRS-Nomenclature
As we know that the QRS-complex is the main part of the ECG so we should deal with a special for it as follows:-
Three things we must keep in our minds.
1.Position of the waves
2.Nature of deflection (+ or -)
3.Size of the deflection.
See the following figures Fig-2; and Fig-3.Fig-4; and Fig-5.
 |
| Fig-2 A normal QRS |
 |
| Fig-3 |
In such cases we should always devise a common theory which states that in any QRS- complex the first negative deflection immediately before the R-waves must be named as Q or q-waves depending upon the size of the deflection. If there are more than one it should be quoted with ' (prime)
Note in the above figure (Fig-3) the Q-wave is absent as there is no first negative deflection before R-wave.
Secondly in any QRS complex any first positive deflection within the complex should be named as R or r waves with ' (prime) if there are more than one according to its sizes.
See the following another typical QRS.
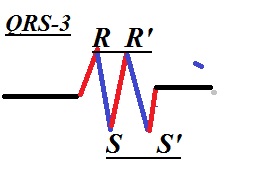 |
| Fig-4 |
Thirdly any first negative deflection immediately after the R-wave is the S or s waves with '(prime)
if more than as per its sizes.
In the above figure (FIG-4) again there are no Q-waves. But there are 2 consecutive positive deflections represents two R-waves (R, R') immediately followed by two consecutive negative deflections named as S and S'.
Then the nomenclature of the T-wave which represents the relaxation of the ventricles.
 |
| Fig-5 |
Continued in next post(F)



