1.ATENOLOL(TENORMIN), PROPRANOLOL(INDERAL) AND CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS(CCB)
Atenolol is a B.P medicine commonly available in the pharmacy under the brand name as Tenormin.
It is technically known under the group as a Beta Receptor Blocker or simply as Beta Blocker.
Briefly we can say that beta-blockers are drugs that lower the blood pressure by lowering the heart rate by blocking beta-1 receptors of the adrenergic nervous system which is more concentrated on the cardiovascular network. The result also included dilation of the blood vessels and reduction of the heart rate.
This drug has notable effects on the ECG if overdosed.
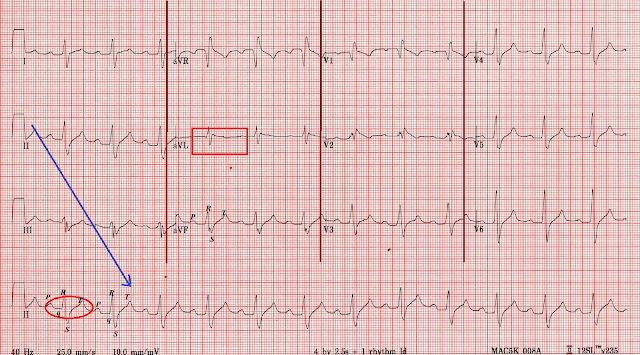
A normal heart rhythm has been shown diagrammatically in Fig-1 above. In that, the waves P, Q, R, S, and T are clear and distinguishable.
Atenolol is a safe B.P medicine with a wider therapeutic index. It is highly water-soluble and is eliminated in the urine. It is less fat-soluble and hence it is less likely to pass into the blood-brain barrier to produce CNS effects.
But as with any other medicine if overdosed or misused by otherwise a normal person atenolol propranolol and any other beta-blocker will reduce heart rate, blood pressure followed by fatal CHF. This can be noticed in the ECG by prolonged PR segment, wider QRS complex, and elevated or depressed ST segment.
This drug has notable effects on the ECG if overdosed.
 |
| Fig-1 |
Atenolol is a safe B.P medicine with a wider therapeutic index. It is highly water-soluble and is eliminated in the urine. It is less fat-soluble and hence it is less likely to pass into the blood-brain barrier to produce CNS effects.
But as with any other medicine if overdosed or misused by otherwise a normal person atenolol propranolol and any other beta-blocker will reduce heart rate, blood pressure followed by fatal CHF. This can be noticed in the ECG by prolonged PR segment, wider QRS complex, and elevated or depressed ST segment.