The autonomic nervous system is pharmacologically divided into two parts as follows
2.Adrenergic N.S.
Both nervous systems are working in a balanced condition. If one system is blocked medically or mechanically then the other system predominates.
But in some areas, one system predominates and in another area, another system predominates according to the necessity and situation.
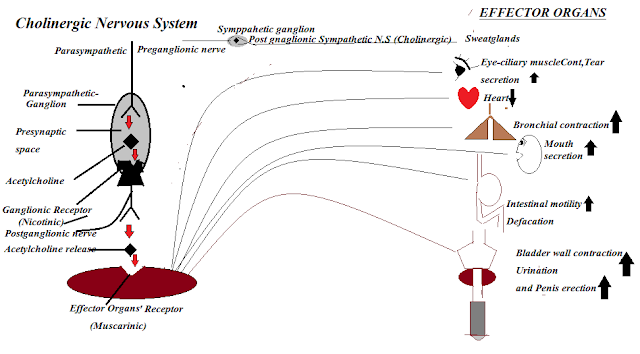
The cholinergic nervous system occupies 99% of the parasympathetic nerve supply except for the one to the sweat glands which is purely sympathetic. Further details on this subject are out of our purpose. In the figure (Fig-1) one can easily understand the supply of cholinergic nerves to various autonomous organs.
Generally in the tranquil conditions the cholinergic N.S. predominates and on contrary in the stressful situations, the adrenergic N.S predominates. Hence the cholinergic N.S is known as the tranquil N.S and the other is known as stressful N.S. For example, in normal situations, the heart is under cholinergic control, and in stressful conditions, the control is shifted to the adrenergic N.S so that the heart rate, the pulse rate, and B.P all increase.
There are many anticholinergic drugs available on the counter of the drug stores and pharmacies that are dispensed as OTC medicines without doctors' prescriptions. The main purpose of this article is to give some detailed warnings about how the patient is affected by the misuse of these drugs.
There are many anticholinergic drugs available at the pharmacy counters as cough syrups, cold and allergy medications, sleeping medicines, psychotic and antipsychotic medications, antidiarrheals and other gastrointestinal disorders medicines, ENT preparations, ophthalmic medicines, etc. etc. These are purchased by the patients either as self medications or by the doctors prescription. Anyhow if these medicines are misused and overused they may produce harmful side effects to the body.
In the above figure (Fig-1), it is clearly mapped that the cholinergic network covers almost all over our body.
The eyes are getting clear visions by the normal cholinergic nerve influence that keeps the moisture content and secretions of the eyes properly and regulate the circular and ciliary muscle contractions to accommodate the vision and the image.
Heart with its beating rate, conduction velocity, atrial contractility and the pulses followed by the blood pressure are kept normal in peaceful situations by the balanced cholinergic influence.
Lungs and the bronchial tree are kept moisturised with their normal secretions and are properly contracted to regulate the rate of respiration, by the balanced influence of the cholinergic nerve supply.
Stomach and intestinal muscles are properly relaxed to improve the digestive system and facilitate the defecation process.
The urinary sphincter muscle is relaxed and the bladder wall is contracted by the cholinergic balanced influence to ease the bladder emptying its urine content.
The sweat glands are supplied with both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system and in both the system the postganglionic neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. The sympathetic cholinergic secretion causes localised sweating and the parasympathetic cholinergic secretion causes generalised sweating and in both cases, the body is facilitated to eliminate the excess heat.
During coital activities, the cholinergic nerve supply to the penis helps it to get sufficient erection and help both the partners to attain orgasm.
The following secretory glands secretions under the balanced influence of the cholinergic nervous system. See the figure above (Fig-1)
1.Sweat glands -They are influenced by both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system in which the postganglionic neuronal transmitter is acetylcholine.
2.Intestinal secretions:- They are increased by the stimulation of the cholinergic nervous system. Thus the cholinergic nervous system speeds up the process of digestion, absorption and excretion.
3.Bronchoial secretions:- These secretions are maintained and increased by the cholinergic nervous system in order to maintain the cleanliness of the respiratory pathway and to regulate the normal respiration.
4.Lacrimal (Tear) secretions:- Cholinergic nervous system help the eyes to clean itself by its secretions and to maintain the correct intra-ophthalmic pressure (IOP).
THE CHOLINERGIC BLOCKADE-ANTICHOLINERGICS:- |
| Fig-2 |
Those drugs which block the muscarinic receptors of the postganglionic cholinergic nervous system are known as anticholinergic agents (See fig-2).
There are many medications which we commonly use with or without doctors' advises including cough syrups have anticholinergic side effects that are undesired to our purpose.
Cough syrups that contain diphenhydramine hydrochloride have anticholinergic side effects and if patients who have any one of the following conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, tachyarrhythmia (heartbeat is higher and irregular), high pulse rate, dry eyes may have moderate to serious consequences.
Constipation and Gastro Oesophagal Reflex Disease are some of the common symptoms of overusing anticholinergics such as tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, imipramine, and clomipramine and Thorazine), anti-Parkinson drug under the brand Cogentin(Benztropine) trihexyphenidyl (Artane), antihistamines (diphenhydramine hydrochloride, chlorpheniramine maleate) and anti-asthmatics (Ipratropium).
There are many anticholinergic such as atropine, scopolamine, homatropine, cyclopentolate, tropicamide and pirenzepine. Atropine is the prototype to this group and is present in Atropa belladonna plant and is a belladonna alkaloid. Atropine, homatropine and scopolamine are used to relieve stomach pain, gastrointestinal spasms and stomach ulcers. If they are overused then they may precipitate anticholinergic unbearable side effects.
Atropine, homatropine, cyclopentolate and tropicamide are also used as eye drops to produce mydriasis (dilatation of the pupil) and cycloplegia (paralysis of the ciliary muscle to relieve pain due to anterior uveitis).
Antihistaminic cough syrups such as diphenhydramine hydrochloride, chlorpheniramine maleate or simply any antihistamine contain anticholinergic effects. Antihistamine fexofenadine containing medicines may have a safe therapeutic index.
Clidinium bromide and chlordiazepoxide are the familiar drugs combination under the brand names Librocol and Librax used for stomach ulcers, stomach cramp, and IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Both the drugs in this combination have anticholinergic effects.
Urinary incontinence (uncontrolled urination due to bladder overactivity) can be treated with the anticholinergic drug known as darifenacin (Trade names Enablex, Emselex)
Dicyclomine + Paracetamol combination under the brand names Baralgan NU, Trigan D, and Spasidex, used for IBS, intestinal and renal colics with abdominal pain is a powerful anticholinergic combination.
Flavoxate under the brand Urispas used for urinary incontinence is an anticholinergic.
Table of anticholinergics with their brand names and uses:-
 |
A-List of Commonly Used Anticholinergics their brand names and Uses
|
Anticholinergic Side Effects 1. Blurred Vision
2.Dry Mouth
3.Urinary Retention (Difficulty in passing urine)
4.Increased and irregular heartbeat.
5.Hypertention
6.Hellucinations, delusions, tinnitus, and dementia
7.Constipation, bowel obstruction
8.Decreased sweating and hyperthermia.
In general, those who are regularly taking medicines such as antipsychotic drugs, antihistaminic drugs to treat allergy, cough, asthma and urticaria must be careful to watch the symptoms of the side effects.
Whenever any drug if you have to take chronically, please get in touch with your doctor intermittently.